Improvements in Gumboro disease with immune complex vaccines
14 June 2021
GUMBOHATCH® is a new immune complex vaccine against Gumboro disease developed by HIPRA. This new immune complex vaccine has introduced a different formulation (IgY of egg origin) and control parameters (free IgY detection and neutralization control) to ensure the complete coating of the IBDV virus. All these new improvements have resulted in a newly formulated immune-complex vaccine, which ensures the maintenance of the maximum potency of the vaccine and consistent results in the field, even in the presence of high levels of maternal antibodies1.
A multicentre, positive-controlled and blind clinical trial was performed with the aim of evaluating the safety and efficacy of GUMBOHATCH®, when administered via the subcutaneous route under field conditions, compared with a standard formulated immune complex vaccine in Europe.
A total of 160,731 one-day-old chicks were vaccinated via the subcutaneous route with GUMBOHATCH® (n= 77,152) or with a standard formulated immune complex vaccine (n=83,579), following the manufacturer’s instructions.
After vaccination, the chicks were distributed to 2 commercial broiler farms in France and to one farm in Belgium.
On each farm the two groups were housed in separate units under identical conditions and monitored up to the end of rearing (35 days of life). Several safety and efficacy parameters were evaluated during this period.
No adverse reactions to either of the two vaccines were observed and similar hatchability and body weight after hatching were also observed in both groups.
Although no Gumboro disease outbreak occurred on any of the farms, general productive parameters were slightly improved (numerically) in the case of houses vaccinated with GUMBOHATCH® (Table 1).
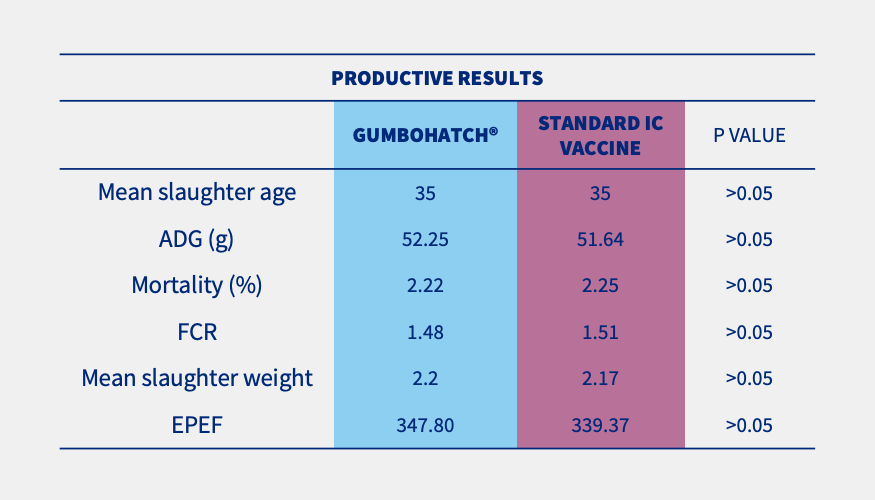 Table 1. Productive results at the end of rearing (35 days of life). Statistically significant differences (p<0.05). *EPEF: European Production Efficiency Factor.
Table 1. Productive results at the end of rearing (35 days of life). Statistically significant differences (p<0.05). *EPEF: European Production Efficiency Factor.
PCR results from bursal imprints (Figure 1) and BB ratio evidenced that the replication of the vaccine virus started from day 21 onwards in both groups.
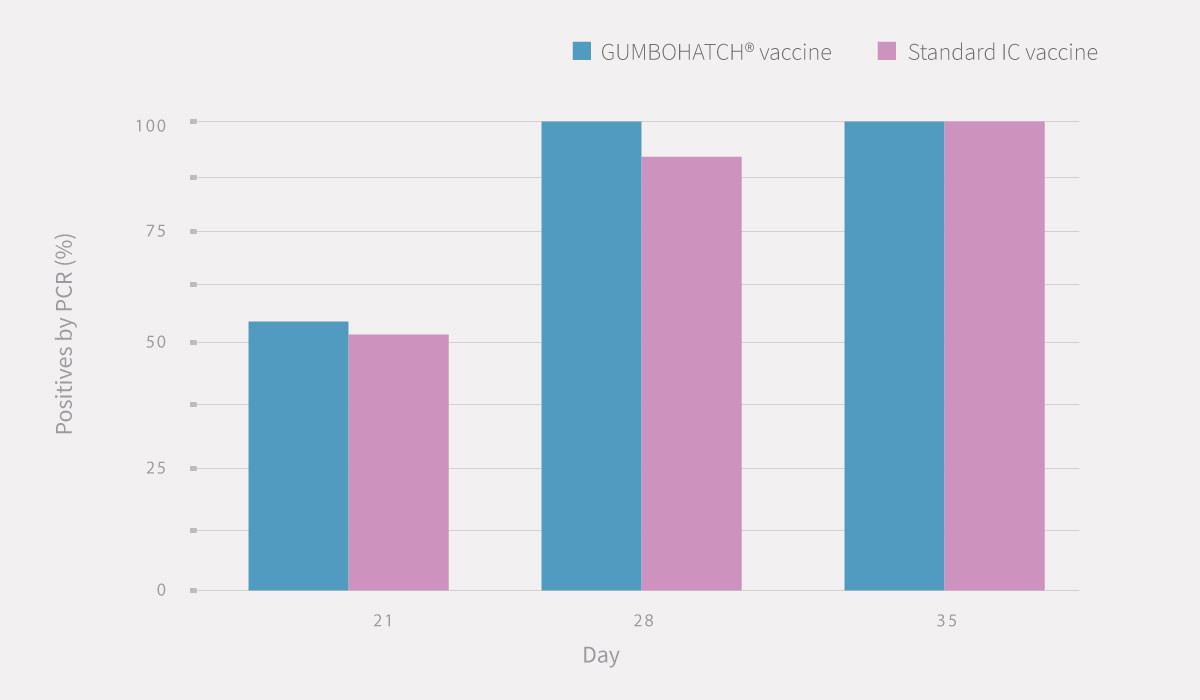
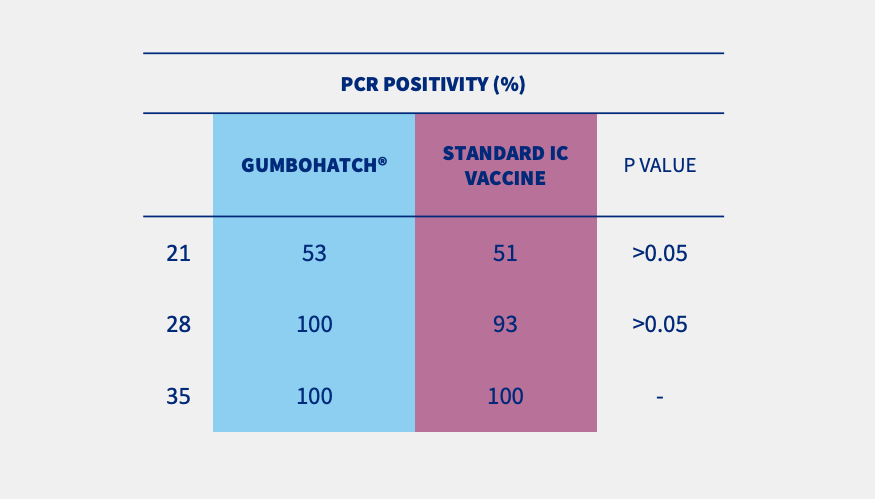 Figure 1. PCR results from bursal imprints. Statistically significant differences (p<0.05).
Figure 1. PCR results from bursal imprints. Statistically significant differences (p<0.05).
The evolution of antibody titres to the IBD virus after vaccination followed a similar pattern in both groups, with a progressive decrease in maternally-derived antibodies between days 0 and 21, followed by a rapid increase in vaccine-induced antibodies from day 28 onwards up to the end of rearing.
However, statistically significant differences (p<0.05) in vaccine-induced antibody titres were detected on days 28 and 35 in favour of the GUMBOHATCH® group, evidencing a faster induction of the humoral protection (Figure 2).
Also, a numerical difference was observed in the percentage of serological positivity between groups, with a higher number of positive animals in the case of GUMBOHATCH® at 28 and 35 days.
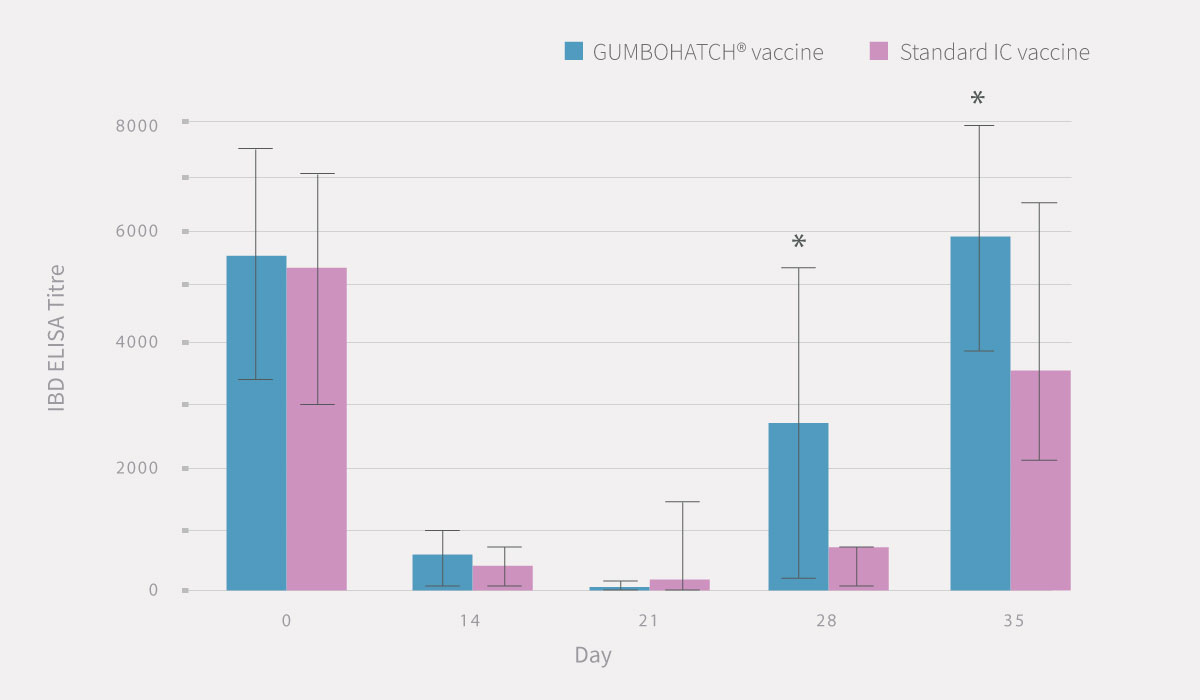
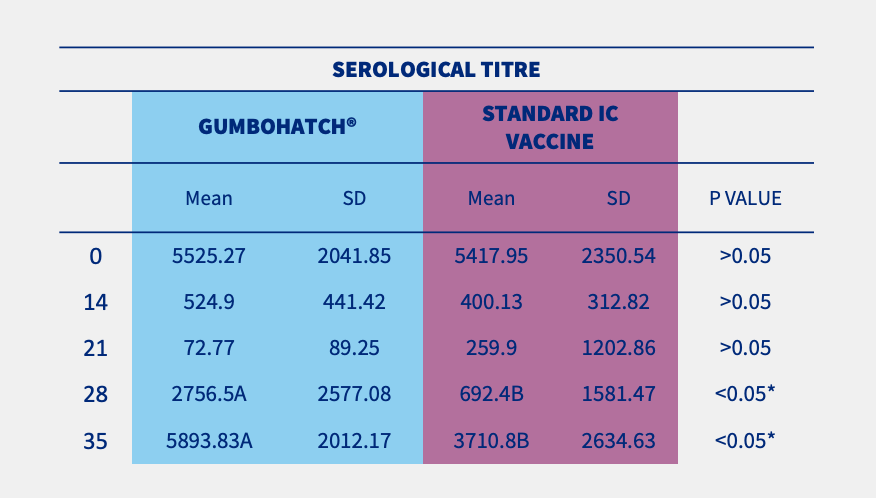
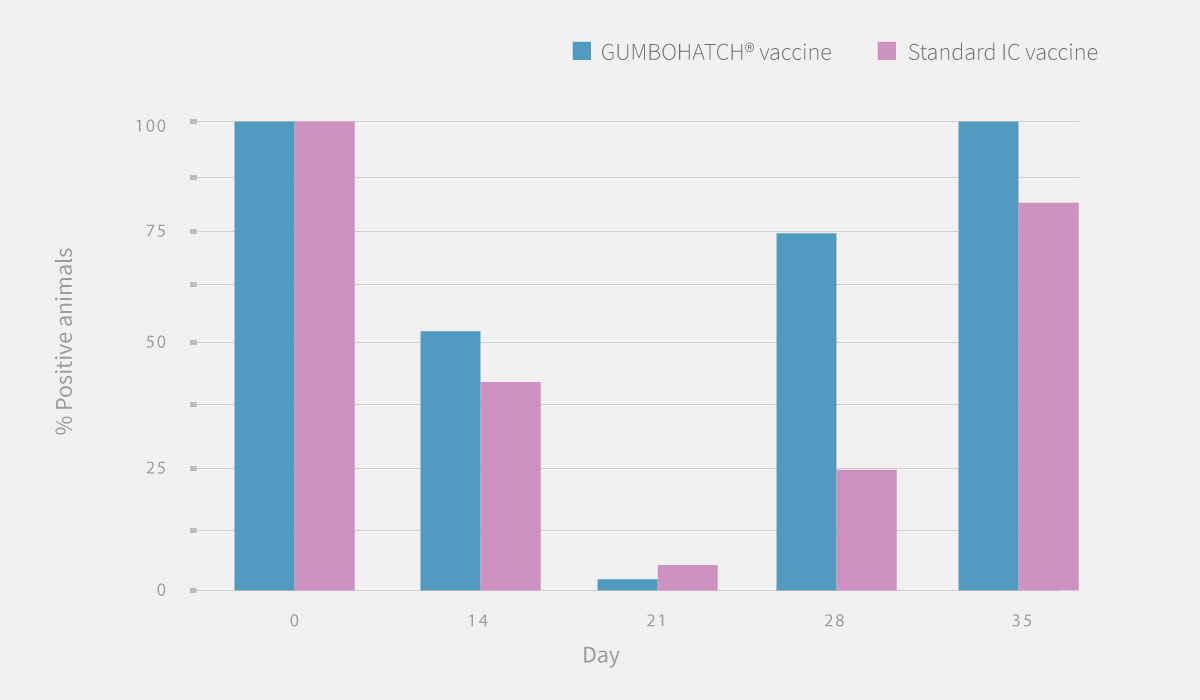
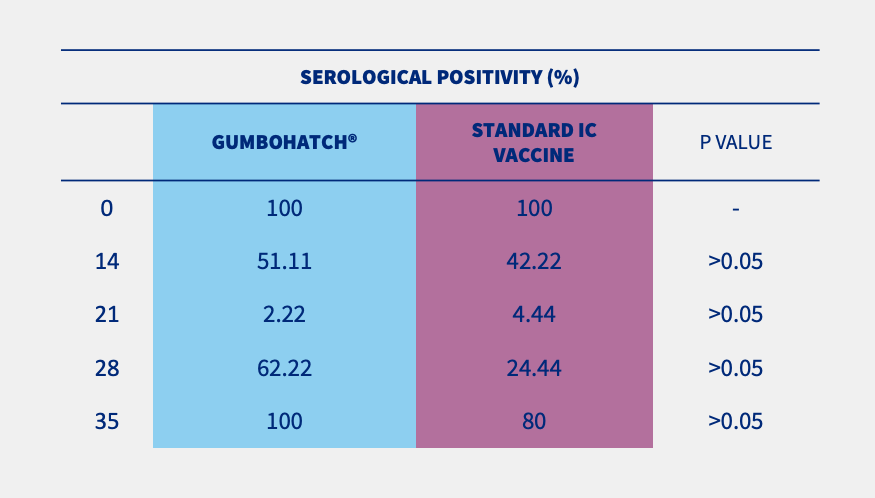 Figure 2. Evolution of serum antibody titres to the IBD Virus; ELISA titre (mean± SEM) (cut-off value =357) (2.A) and evolution of serological positivity (2.B). *Statistically significant differences (p<0.05).
Figure 2. Evolution of serum antibody titres to the IBD Virus; ELISA titre (mean± SEM) (cut-off value =357) (2.A) and evolution of serological positivity (2.B). *Statistically significant differences (p<0.05).
The results obtained in this study allow the conclusion to be drawn that vaccination with GUMBOHATCH® is safe and confers a faster humoral protection against Gumboro disease when compared with a standard-formulated immune complex vaccine. The more rapid humoral response observed with GUMBOHATCH® compared to a standard formulated vaccine, may correspond to the new formulation and controls performed that prevent the neutralization of the vaccine virus when in contact with high levels of maternal antibodies.
References:
Don't miss any updates
Controller: LABORATORIOS HIPRA, S.A.
Purposes: Managing the contractual and/or business relationship with HIPRA, including sending news, promotions and invitations to events sponsored by HIPRA.
Lawful basis: Performance of the contractual relationship and HIPRA’s legitimate Interest.
Recipients: Third parties to which HIPRA has entrusted cloud computing, security, auditing, mailing, technical and computer support services, as well as companies in its group.
Rights: Request access to and rectification or erasure of personal data and other rights as explained in the additional information. You can seeview the detailed additional information about data protection in our Privacy Policy.
For further information, please check our detailed information on Data Protection.